Welding/Torch cutting Shades
[additional
information]
 Shades in the form of goggles, hand-held shields, or helmets are necessary when you are
welding, brazing, or torch-cutting, or when such work is being performed near you.
These operations produce
Shades in the form of goggles, hand-held shields, or helmets are necessary when you are
welding, brazing, or torch-cutting, or when such work is being performed near you.
These operations produce 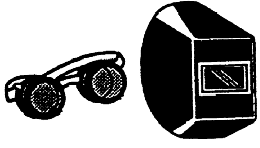 radiation of wavelengths and intensities that can seriously damage
the eyes. radiation of wavelengths and intensities that can seriously damage
the eyes.
 See the two
tables reproduced below for protection recommended and shade values. Higher shade numbers
represent a darker filter for use with more intense light sources. The welding helmet does
not provide adequate protection against flying sparks and debris, and must be supplemented with
other eye protection. The hazard
assessment for your welding, brazing, or torch cutting operation should prescribe the
combination of filter lenses, headgear, and impact goggles/sideshields/glasses that will
be necessary for your overall eye/face/head protection from heat, fire, and sparks or
other flying objects. See the two
tables reproduced below for protection recommended and shade values. Higher shade numbers
represent a darker filter for use with more intense light sources. The welding helmet does
not provide adequate protection against flying sparks and debris, and must be supplemented with
other eye protection. The hazard
assessment for your welding, brazing, or torch cutting operation should prescribe the
combination of filter lenses, headgear, and impact goggles/sideshields/glasses that will
be necessary for your overall eye/face/head protection from heat, fire, and sparks or
other flying objects.
 Helmet
or goggles have been donned properly when they are comfortably situated on head and face
in a position that prevents the possibility of exposure of the eyes to the radiant energy
emitted by the process. Visually inspect the PPE for damage (cracks, scratches, torn
or worn elastic band) before use and after removal. Do not use eyewear with defects
or weaknesses. If it is necessary to lift your helmet in the presence of a flame or
arc, use a hand-held shade filter to cover your eyes. Helmet
or goggles have been donned properly when they are comfortably situated on head and face
in a position that prevents the possibility of exposure of the eyes to the radiant energy
emitted by the process. Visually inspect the PPE for damage (cracks, scratches, torn
or worn elastic band) before use and after removal. Do not use eyewear with defects
or weaknesses. If it is necessary to lift your helmet in the presence of a flame or
arc, use a hand-held shade filter to cover your eyes.
 Filter lenses will only protect your eyes if you use the proper minimum shade and
if you only view the radiant energy source through the filter.
Keep your eyes covered.
Filter lenses will only protect your eyes if you use the proper minimum shade and
if you only view the radiant energy source through the filter.
Keep your eyes covered.
 Read
manufacturer's instructions for care and maintenance, and keep items clean. If no
manufacturers instructions are available, clean with mild soap and water. Store in
a protected, dry, temperate location to protect from damage. Hanging goggles from
their elastic band will cause unnecessary wear on the band, causing it to loose its
elasticity and fail. Avoid laying helmets or goggles down in a manner that could
scratch the lenses. Read
manufacturer's instructions for care and maintenance, and keep items clean. If no
manufacturers instructions are available, clean with mild soap and water. Store in
a protected, dry, temperate location to protect from damage. Hanging goggles from
their elastic band will cause unnecessary wear on the band, causing it to loose its
elasticity and fail. Avoid laying helmets or goggles down in a manner that could
scratch the lenses.
|